India has achieved a significant milestone in its renewable energy journey, with the number of jobs in the sector soaring to an estimated 1.02 million in 2023. According to the 2024 Annual Review by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), this surge highlights India’s commitment to a sustainable energy future, while also showcasing the country’s role in driving global growth in renewable energy employment. This development is part of a larger global trend, with the worldwide renewable energy workforce growing to 16.2 million in 2023, up from 13.7 million in 2022.
India’s leadership in renewable energy is not only helping to reduce its carbon footprint but is also proving to be an engine for economic growth. The green jobs being created are crucial in shaping a future that emphasizes sustainability while generating significant employment opportunities across the nation. As India transitions towards energy independence and environmental sustainability, these jobs are providing livelihoods for millions and helping to reduce the country’s reliance on fossil fuels.
IRENA’s renewable energy and jobs series

The IRENA Renewable Energy and Jobs series offers an in-depth look at the employment trends within the global renewable energy sector. Since its inception in 2011, the series has been a key component of IRENA’s broader analysis of the socio-economic impacts of transitioning to renewable energy. The reports cover a range of topics, including job creation, skill development, gender equity in the workforce, and the development of local capacities.
Each edition of the series presents up-to-date data, examining employment in various renewable energy technologies and the policies that support job growth. The series also assesses the educational and skill requirements within the sector, although detailed information on workforce attributes remains limited. One of the key themes of the series is the need for “decent work” to ensure that the transition to renewable energy is both fair and inclusive.
The 2024 edition of the report places a strong emphasis on employment in energy access, women’s participation in the renewable workforce, and the role of renewable energy in achieving a just transition. Projections up to 2050 are included, outlining the potential impacts of renewable energy pathways on jobs, GDP, and overall human welfare.
India’s renewable energy workforce in 2023
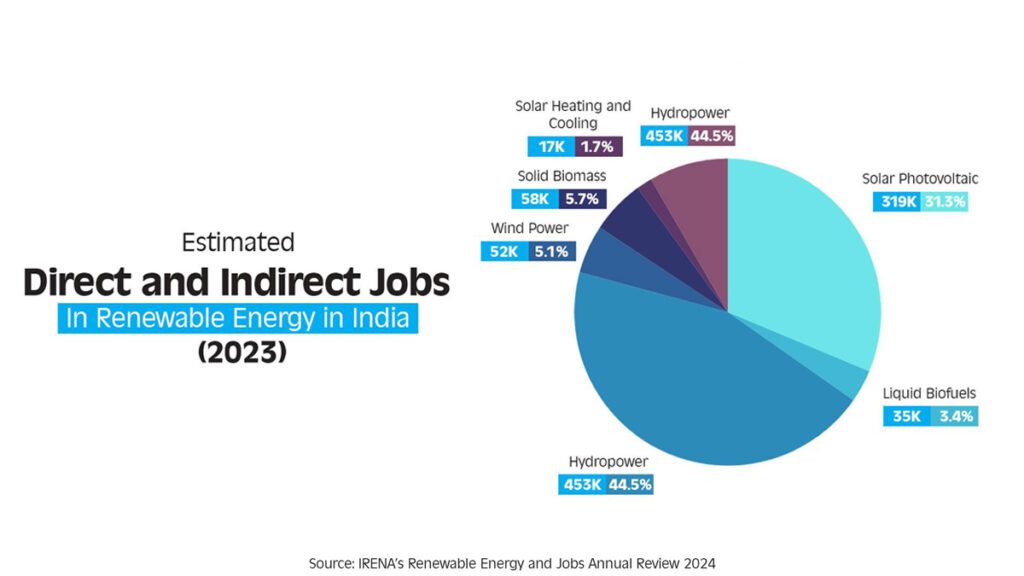
In 2023, India had an estimated 1.02 million jobs in the renewable energy sector, making a substantial contribution to the global workforce. The sector’s largest employer was hydropower, which provided around 453,000 jobs in India, accounting for 20% of the global total. India ranked second only to China in terms of hydropower employment.
Solar energy was another major contributor to job creation in India, with around 318,600 people employed in the solar photovoltaic (PV) sector. In 2023, India added 9.7 GW of solar PV capacity, bringing its cumulative solar capacity to 72.7 GW by the end of the year. India’s solar module manufacturing capacity stood at 46 GW in 2023, and it is expected to grow to 58 GW in 2024, making India the second-largest PV manufacturer globally after China.
The solar PV sector saw an 18% increase in grid-connected solar jobs in 2023, with around 238,000 people employed in this area. The off-grid solar sector employed an additional 80,000 people, highlighting the diverse nature of job opportunities within the solar industry.
India’s wind energy sector also made significant strides in 2023, with a cumulative installed capacity of 44.7 GW. The country added 2.8 GW of new wind capacity during the year, marking a significant increase after several years of slower growth. Wind energy provided employment to approximately 52,200 people in 2023, with the majority of these jobs concentrated in operations and maintenance, as well as construction and installation.
Other renewable energy sectors, such as biofuels, biomass, and biogas, also contributed to job creation in India. The liquid biofuels sector provided 35,000 jobs, while the solid biomass sector accounted for 58,000 jobs. The biogas sector created employment for 85,000 people, further underscoring the breadth of job opportunities within the renewable energy industry.
Government initiatives driving job creation
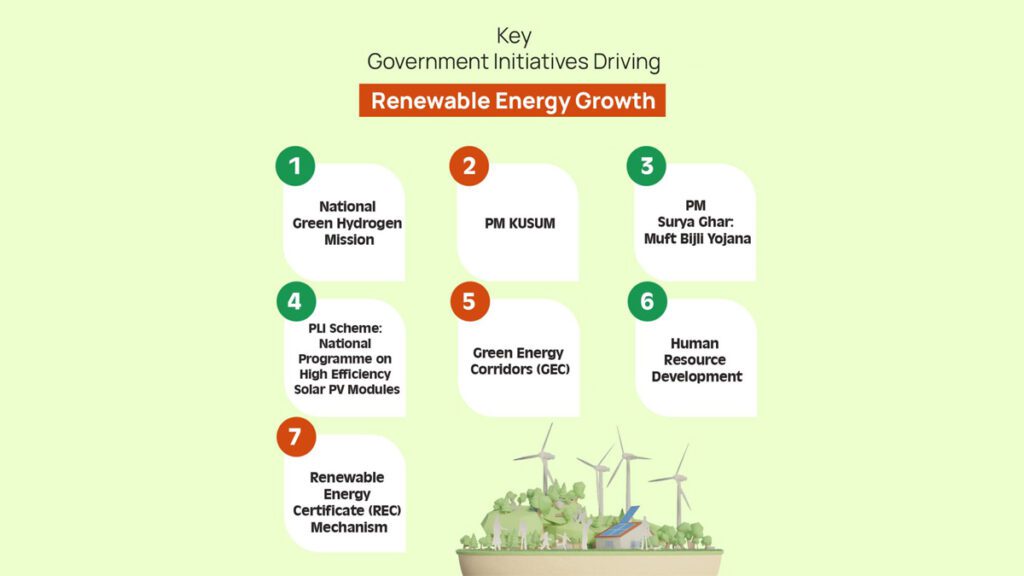
India’s renewable energy job growth can be attributed in large part to the country’s ambitious government initiatives, which aim to accelerate the transition to a sustainable energy future. Key programs include the National Green Hydrogen Mission, PM-KUSUM, PM Surya Ghar, and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for solar PV modules.
The National Green Hydrogen Mission, approved in January 2023, is a cornerstone of India’s strategy to become a global leader in the production and export of green hydrogen. The mission aims to decarbonize key sectors, reduce the country’s dependence on imported fossil fuels, and create jobs across the green hydrogen value chain. With a target of producing at least 5 million metric tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2030, the mission is expected to generate numerous employment opportunities while advancing India’s renewable energy workforce.
Another important initiative is the PM-KUSUM scheme, which was launched in 2019 and scaled up in January 2024. This program aims to provide energy and water security to farmers, while also promoting the use of solar energy in the agricultural sector. The PM-KUSUM scheme is expected to add 34,800 MW of solar capacity by March 2026 and create an estimated 7.55 lakh job-years for skilled and unskilled workers.
The PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, launched in February 2024, is another significant initiative aimed at transforming India’s energy landscape. The scheme provides free electricity to households by subsidizing the installation of rooftop solar panels. It is expected to benefit 1 crore households and generate savings of ₹75,000 crores annually in government electricity costs. In addition to its environmental benefits, the scheme is projected to create around 17 lakh direct jobs across sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, installation, and maintenance.
The PLI scheme for high-efficiency solar PV modules is also a key driver of job creation in India. With an outlay of ₹24,000 crore, the scheme aims to build Giga Watt-scale manufacturing capacity in India, reduce import dependence, and create employment opportunities in the solar manufacturing sector.
The future of renewable energy jobs in India

India’s renewable energy sector is poised for continued growth, with employment opportunities expected to increase as the country ramps up its efforts to achieve energy independence. Government initiatives, such as the National Green Hydrogen Mission, PM-KUSUM, PM Surya Ghar, and the PLI scheme, are expected to play a critical role in driving job creation and fostering a skilled workforce.
The diverse range of job opportunities within the renewable energy sector, from hydropower and solar PV to wind energy and biomass, highlights the sector’s potential to provide sustainable livelihoods for millions of Indians. As India continues to invest in renewable energy technologies, it is also building the necessary infrastructure and workforce to support a greener future.
The rapid expansion of India’s renewable energy sector is not only helping the country meet its environmental goals but is also driving significant economic growth and job creation. The 1.02 million jobs created in 2023 are a testament to the sector’s potential to transform India’s energy landscape while providing sustainable livelihoods for millions of people.












